Calibrator
Prepare for calibration
Please take a look at the section Connect to the robot.
The rationale for calibration
Understand the zero state and the coordinate system
After the robot enters the calibration state, with all servos rotated to their zero angles, attach the head, tail, and legs prepared in the previous section to the body. They are generally perpendicular to their linked body frames.

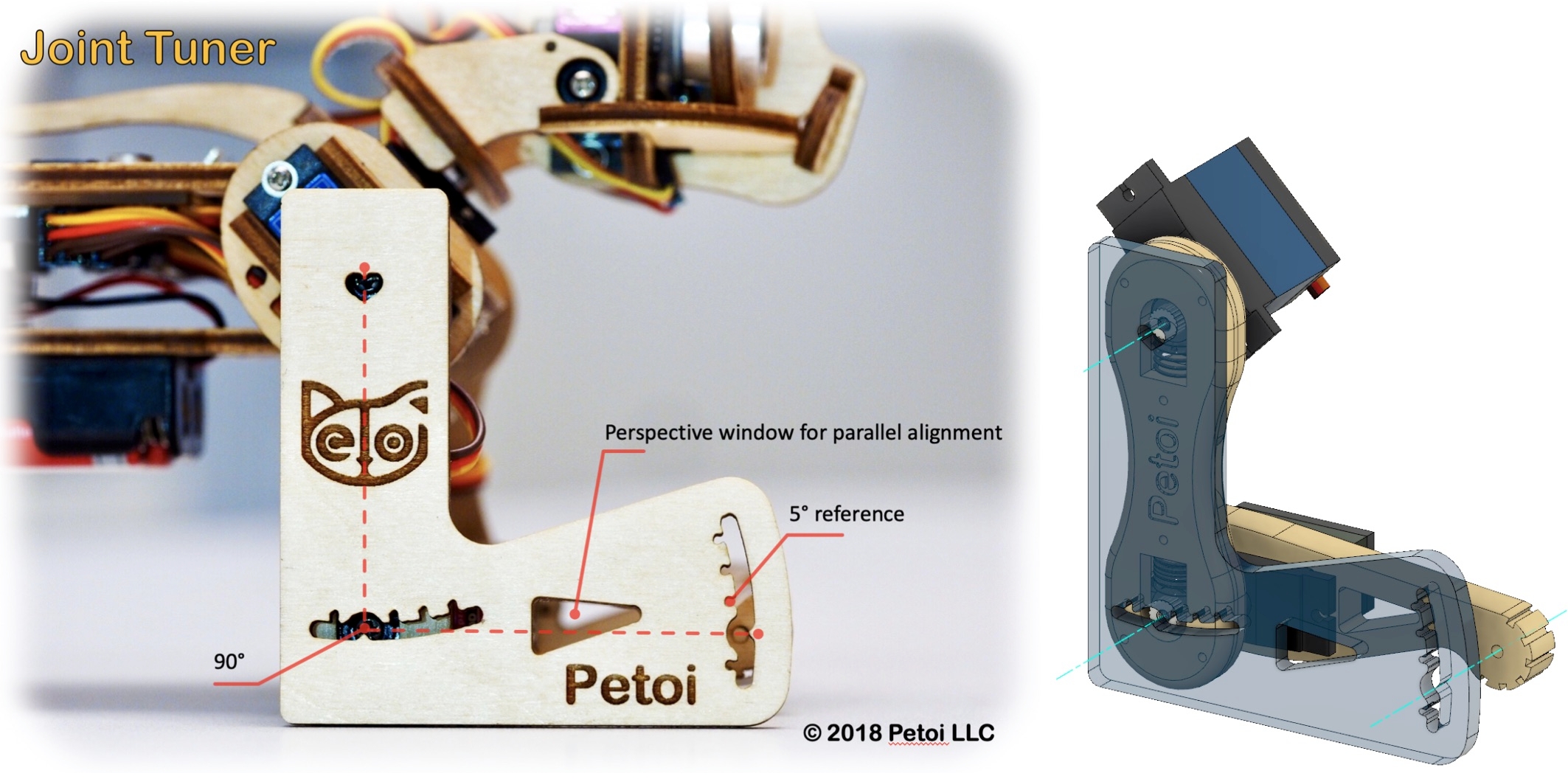
Install the servo-related components according to the picture above and try to ensure that they are perpendicular to each other (the upper leg is perpendicular to the torso, and the lower leg is perpendicular to the upper leg).
Note: Insert the servo-related components directly into the servo output shaft; do not turn the output shaft during this process.
Rotating the limbs counter-clockwise from their zero states will be positive (same as in polar coordinates). Viewed from the left side of the robot's body, the counter-clockwise rotation of the joint is defined as the positive direction.
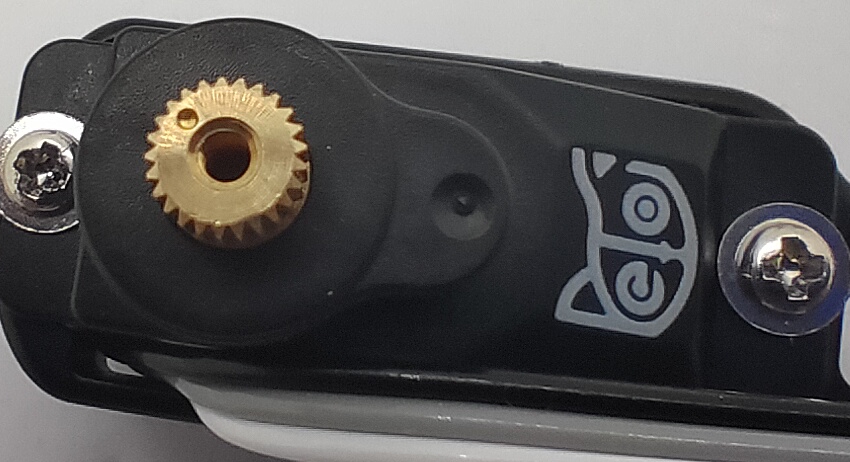
Discrete angular intervals
If we look closer at the servo shaft, we can see it has a certain number of teeth. That’s for attaching the servo arms and avoiding sliding in the rotational direction. In our servo sample, the gears divide 360 degrees into 25 sectors, each taking 14.4 degrees(offset of -7.2~7.2 degrees). That means we cannot always get a perfect perpendicular installation.

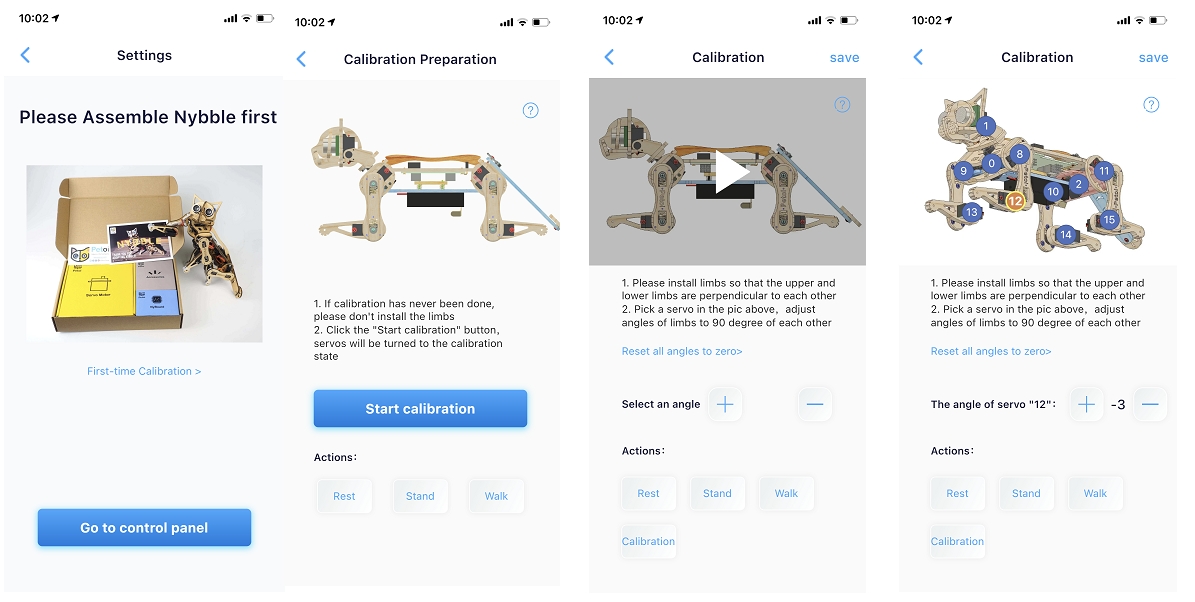
Calibration Interfaces
The calibrator interface for Nybble is as following, this interfaces will be displayed when you calibrate for the first time:
Enter the calibration state
After the battery powers on the robot, there are two methods to enter the calibration state.
Click the Start Calibration button.

Click the Calibration button in the calibration interface.

Use the included L-shaped tool as a reference

First, select the index number of the joint servo from the diagram(when adjusting the leg servo, adjust the thigh first, and then adjust the calf).
Then, click the "+" or "-" button to fine-tune the joint to the desired angle.
Test the calibration effect

You can click the skill buttons to switch between Rest, Stand, and Walk to test the calibration effect.
If you want to continue calibrating, please click the Calibration button, and the robot will return to the calibration state, with all servos immediately moving to their calibration positions.
After calibration, remember to click the Save button to save the calibration offset. Otherwise, click "<" in the upper left corner to abandon the calibration.
Install the screws for construction kit
For the construction kit, after completing the joint calibration, install the center screws to fix the leg parts and servo gears.
Last updated