Joint Calibrator
Robots can be precisely calibrated using the Petoi Desktop App.
** Download the latest version of the Petoi Desktop APP. **
Petoi Desktop App works on both Nybble and Bittle controlled by NyBoard based on ATmega328P or Bittle X controlled by BiBoard based on ESP32.
Prepare for calibration
Plug in the battery and press the battery button for 3 seconds to power on the robot.
There are two methods to connect to the computer:
The USB data cable connection must be made directly to the BiBoard, not to the battery's charging port.
You can also connect to the computer via Bluetooth.
For BiBoard, please ensure the program enters the regular startup mode.
This robotic arm is already fully assembled.
For the pre-assembled kit, install the neck servo in the servo slot using two M2 x 5 self-tapping screws. Then you can do the fine-tuning.

The rationale for calibration
Understand the zero state and the coordinate system
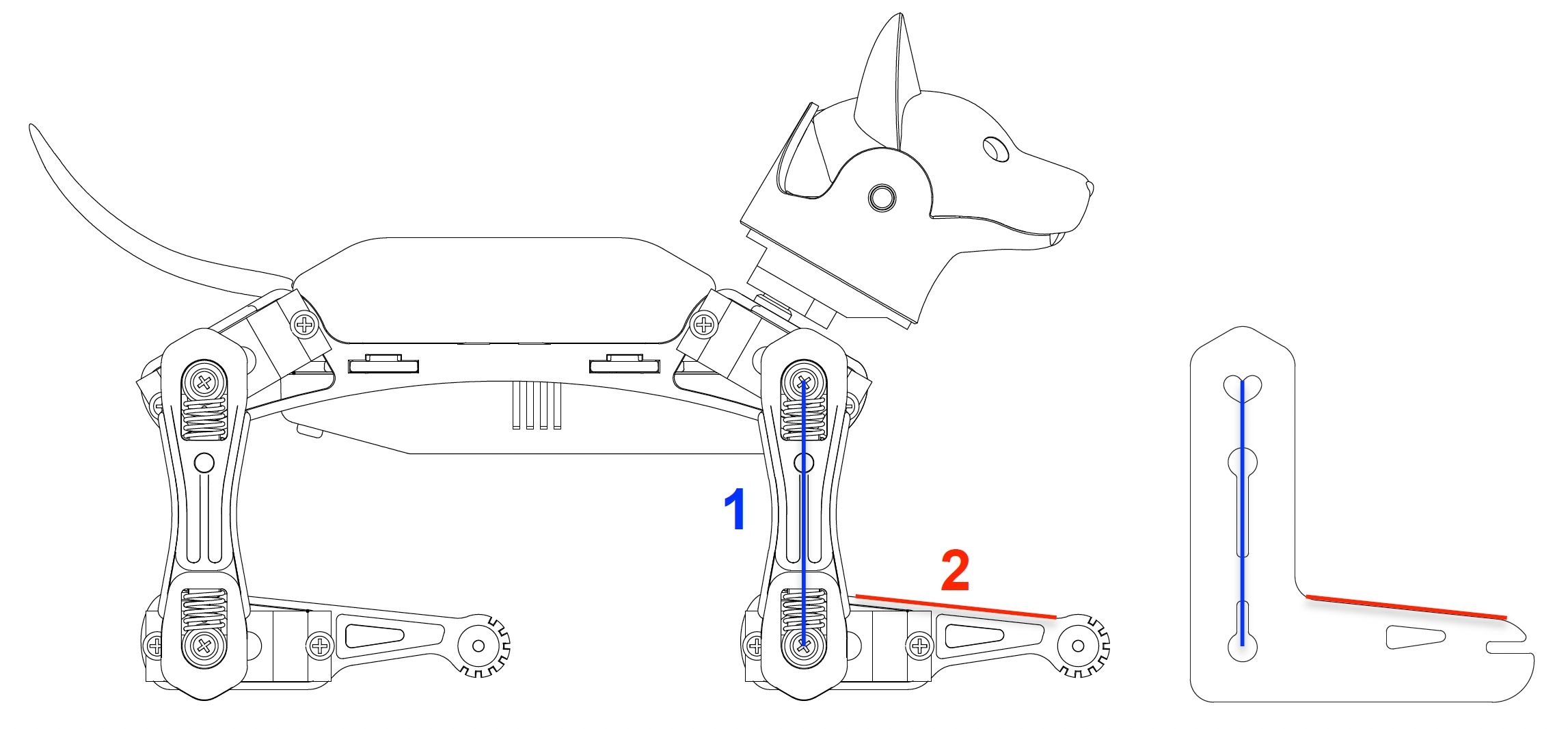
After entering the calibration state, with all servos rotated to their zero angles, attach the head, tail, and legs prepared in the previous section to the body. They are generally perpendicular to their linked body frames. The calibration pose is shown below:
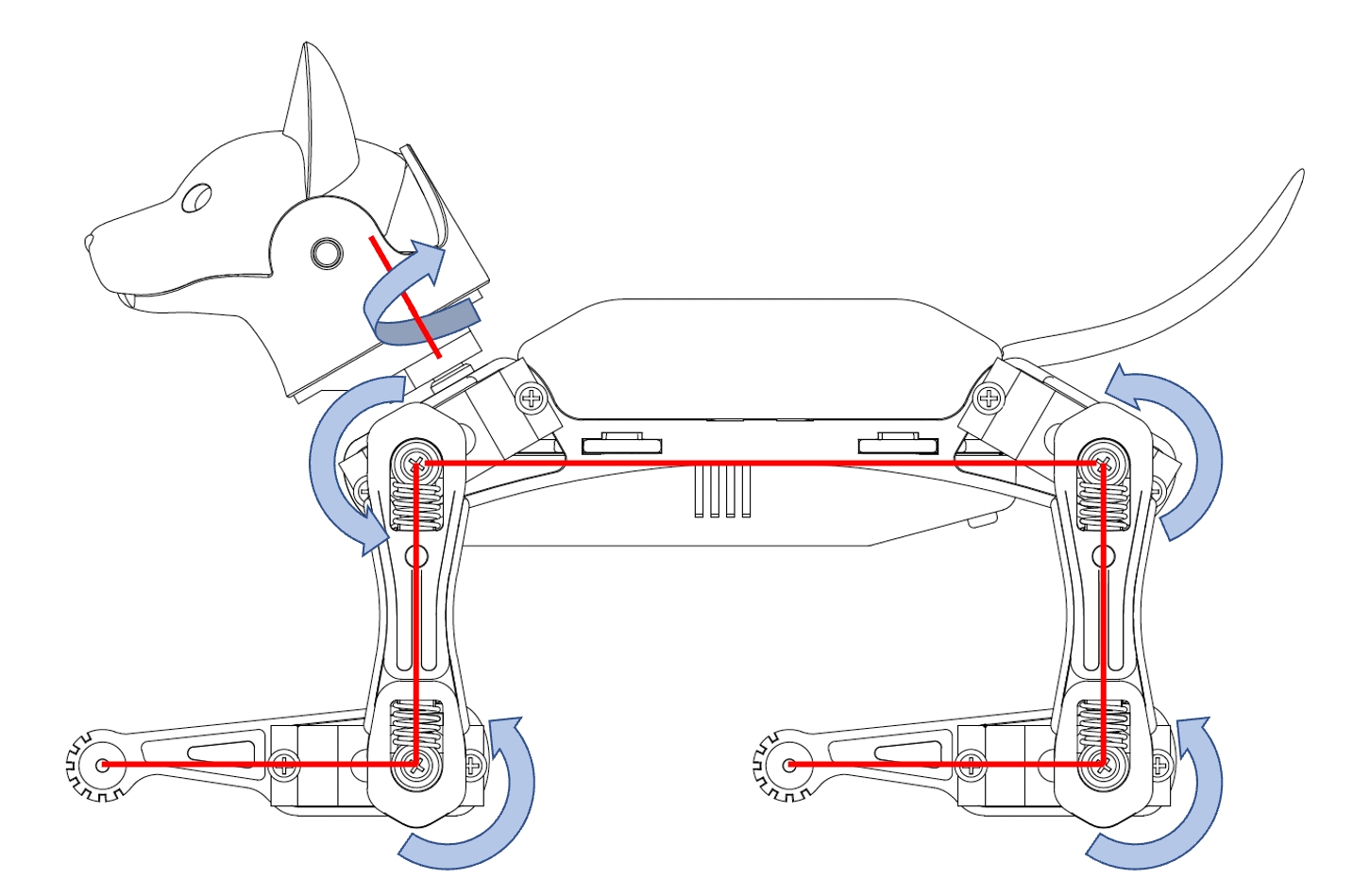
Install the servo-related components according to the picture (calibration state) and try to ensure that they are perpendicular to each other (the upper leg is perpendicular to the torso, and the lower leg is perpendicular to the upper leg).
Note: Insert the servo-related components directly into the servo output shaft; do not turn the output shaft during this process.
Rotating the limbs counter-clockwise from their zero states will be positive (same as in polar coordinates). Viewed from the left side of the robot's body, the counter-clockwise rotation of the joint is defined as the positive direction.
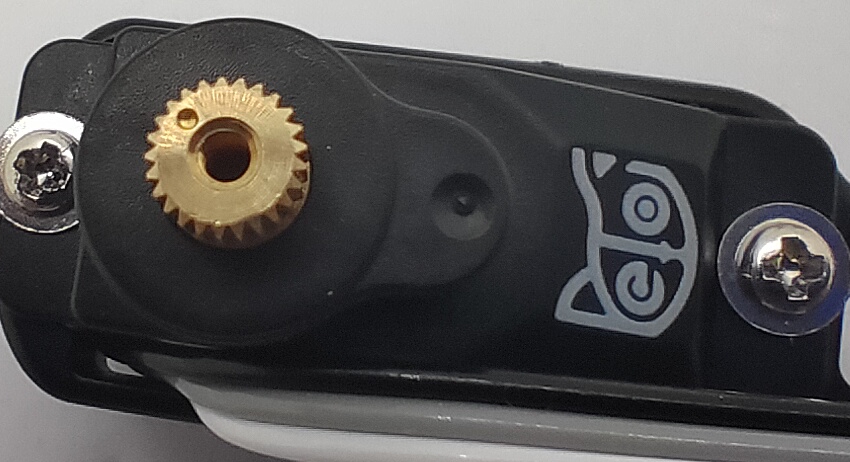
Discrete angular intervals
If we look closer at the servo shaft, we can see it has a certain number of teeth. That’s for attaching the servo arms and avoiding sliding in the rotational direction. In our servo sample, the gears divide 360 degrees into 25 sectors, each taking 14.4 degrees(offset of -7.2~7.2 degrees). That means we cannot always get a perfect perpendicular installation.

Calibration process
Enter the calibration state
After a battery powers on the robot, there are two methods to enter the calibration state:
It will enter the calibration state automatically when you click the Joint Calibrator button.
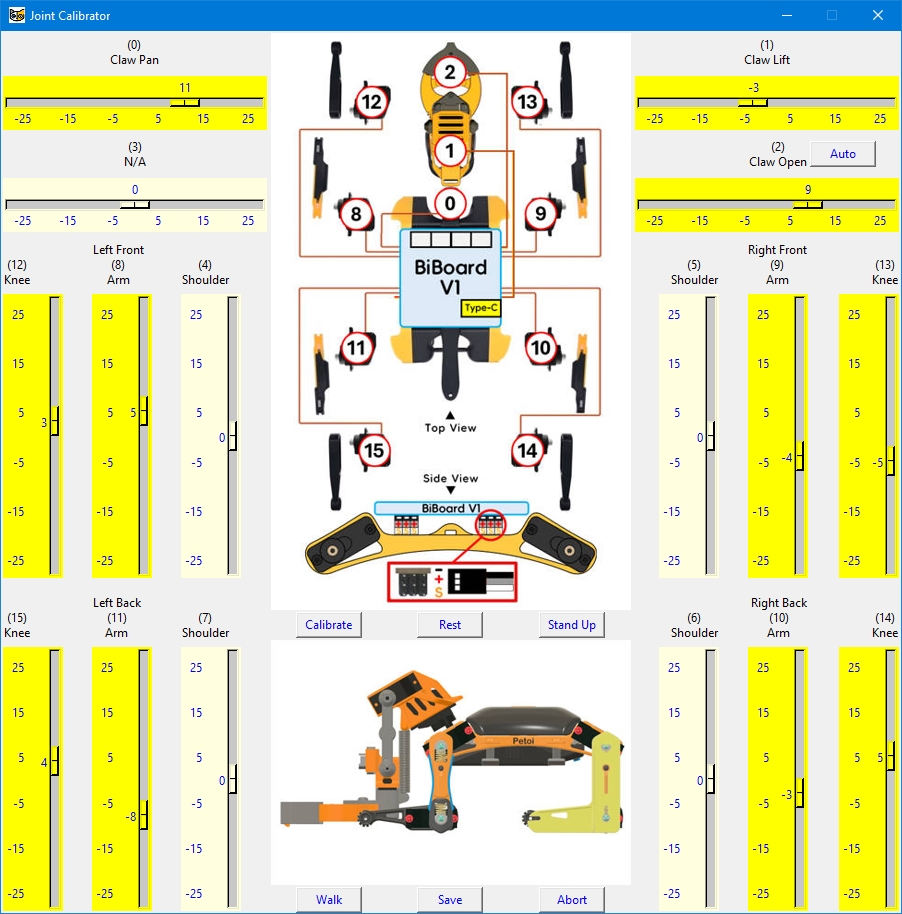
Click the Calibrate button in the Joint Calibrator interface.
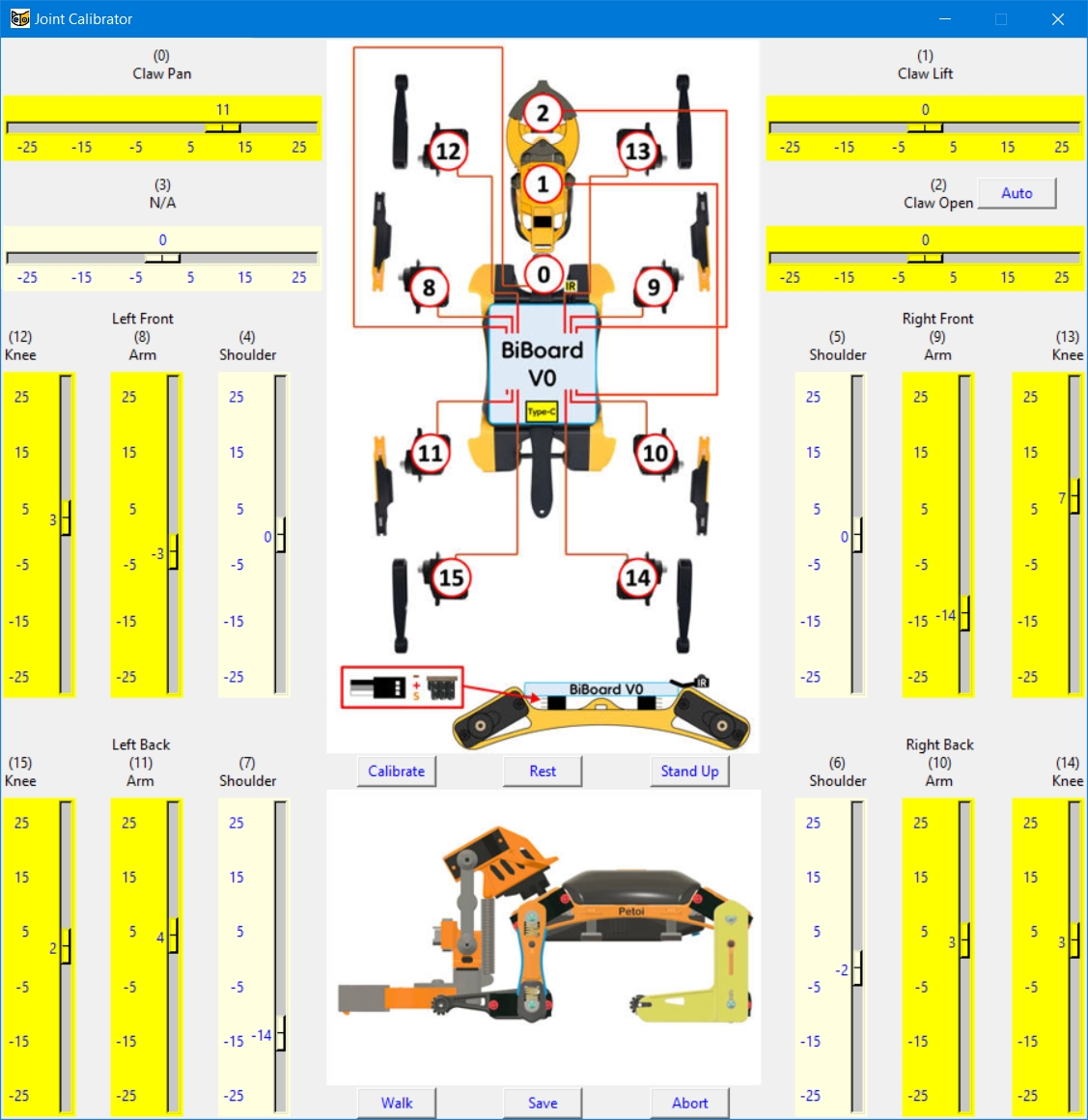
The joint calibration interface for Bittle X+Arm, which uses BiBoard V1 in the Petoi Desktop App, is as follows:
Some customers already have Bittle X (BiBoard V0), which can also be equipped with a robotic arm. The joint calibrator interface is as follows. Please note the wiring of the servo:
Installing and Fine-tuning
Please disregard the type of mainboard in the following installation pictures, as all Petoi mainboards have the same size.
For the Construction kit, after entering the calibration state, please install the neck servo and legs as follows:
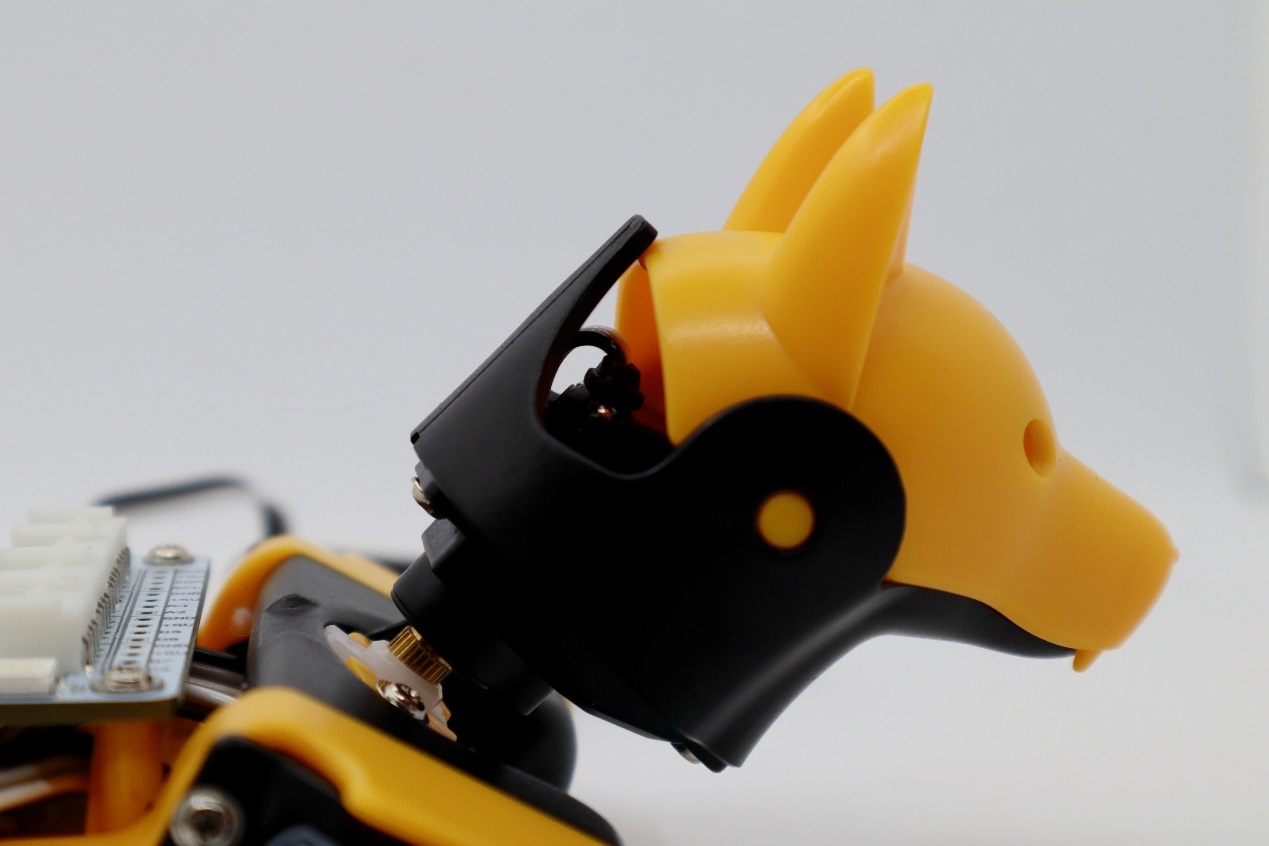
Install the neck servo
Note: For Bittle X+Arm, there is no head component; only need to install the neck servo which is in the head of Bittle X's.
In the calibration state, place the head as close to the central axis as possible and insert its servo shaft into the servo arm of the neck.
Press down on the head so it is firmly attached to the neck.

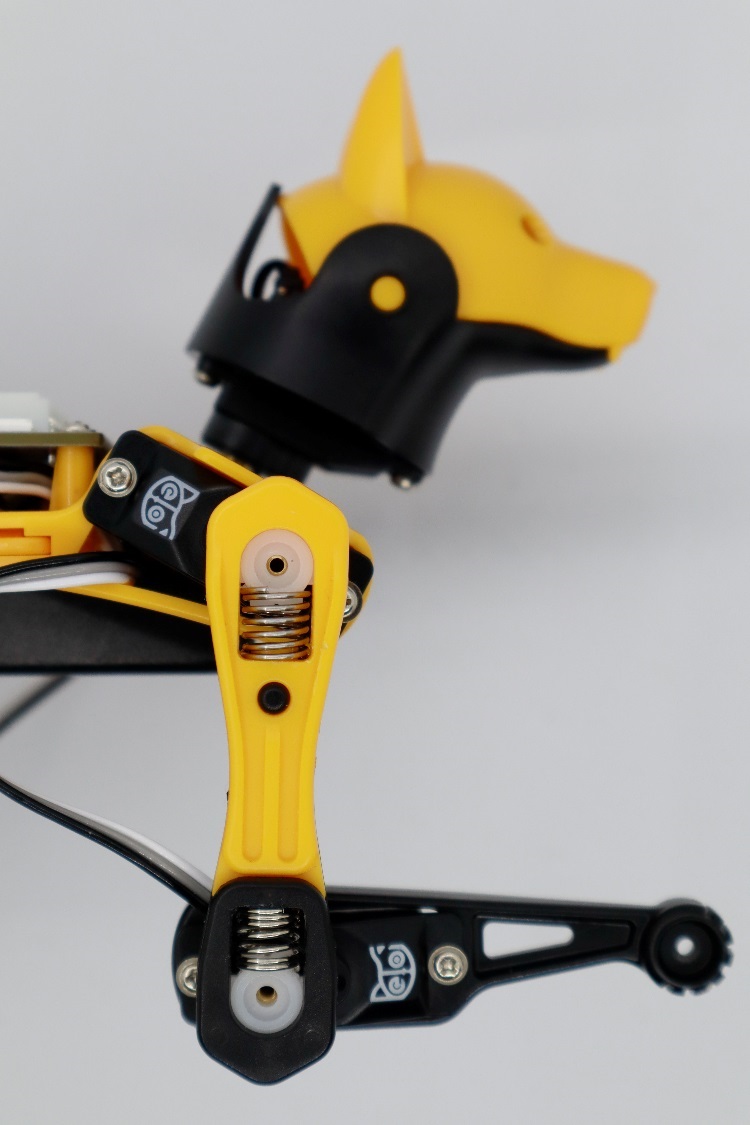
Install the legs
Install the upper leg and lower leg components to the output teeth of the servos after the Bittle is powered on and in the calibrated neutral position. Please keep the torso, upper leg, and lower leg installed vertically as much as possible. Do not install the lower leg backward, as shown in the picture.

Install the robotic arm
The robotic arm installation of the construction kit is the same as the pre-assembled kit.
Fine-tuning
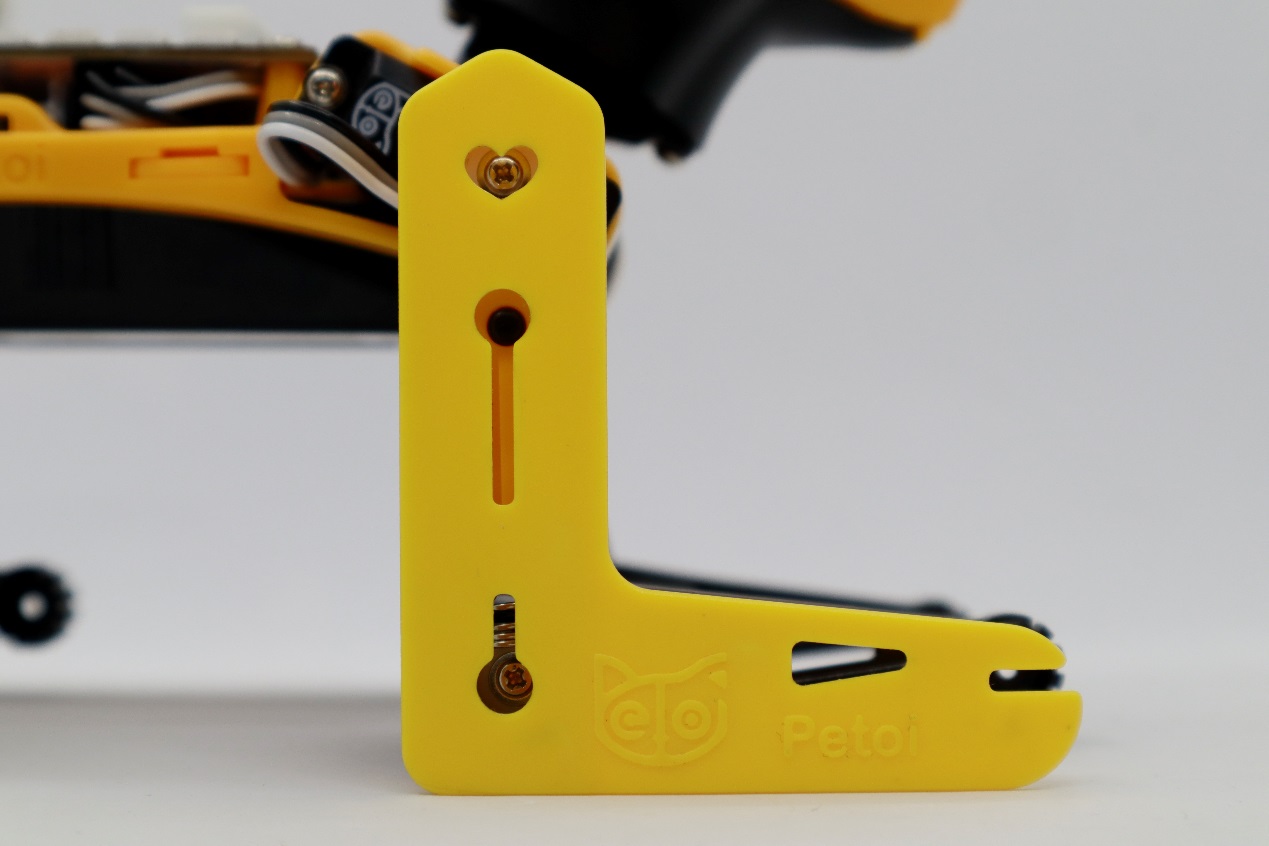
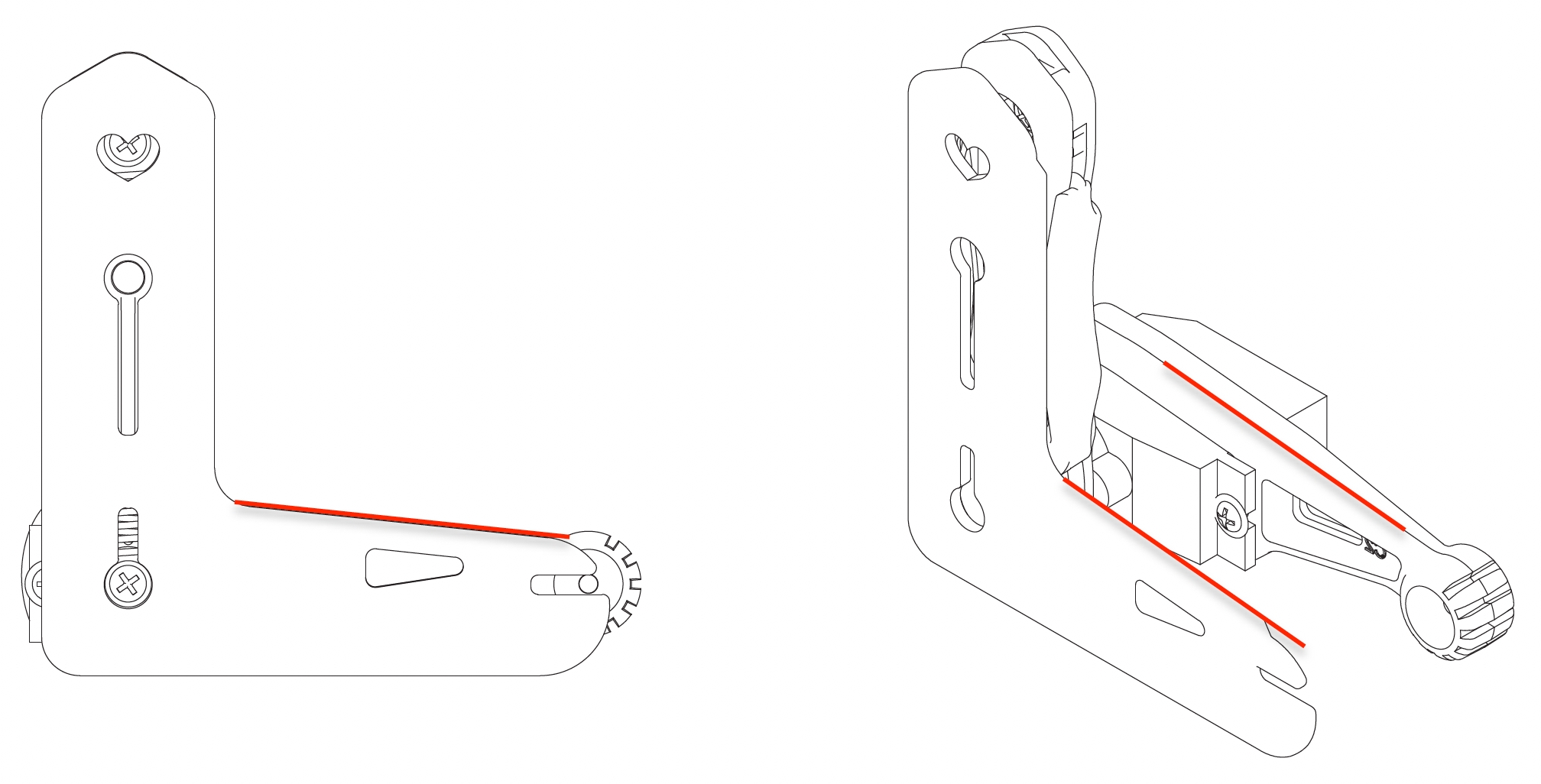
Please use the L-shaped calibration tool included in the package as a calibration reference. According to the joint numbers shown in the picture within the calibration interface, drag the corresponding sliders or click on the blank areas of the slider tracks to fine-tune the joints to a right angle.
Please note that when calibrating the servos, adjust the upper leg first, then change the lower leg.


The process of fine-tuning the legs and the neck servo (joint index 0) is the same as that of Bittle / Bittle X's (as above).
Please click the blank part of the slider track and follow the calibration posture below to fine-tune Servo 1 on the robotic arm.
Please click the Auto button to fine-tune the claw servo (joint index 2) on the robotic arm.
You can also manually click the blank part of the corresponding slider track and adjust the gear on the servo output shaft to the position shown in the figure above.
Validation and Save data
You can switch between "Rest", "Stand up" and "Walk" to test the calibration effect.
If you want to continue calibrating, please click the Calibration button, and the robot will be in the calibration state again (all servos will move to the calibration position immediately).
Note: You may need a second round of calibrations to achieve optimal results.
After calibration, remember to click the "Save" button to save the calibration offset. Otherwise, click the "Abort" button to abandon the calibration data. You can save the calibration in the middle in case your connection is interrupted.
Install the screws for the construction kit
After completing the joint calibration, install the center screws to fix the components and servo gears.
Last updated